Swiss Hiking Signposts
Switzerland has an extensive hiking trail network with 65000 kilometers of signed hiking trails. There are three kinds of trails: hiking trails (marked in yellow), mountain hiking trails (marked in yellow-red-white), and alpine hiking trails (marked in white and blue).
The trails are signed with four kinds of signs, amongst them hiking signposts.
Let's compose those signs with PyTamaro!
Before doing this activity you should do the
Swiss Hiking Direction Pointers
activity, as you will need to reuse some functions that you have developed there.
Colors
The hiking signpost colors are specified in the handbook of hiking trail signage, and are the following:
- RAL 9016 "traffic white": RGB: 241-241-234
- RAL 3020 "traffic red": RGB 187-31-17
- RAL 1007 "daffodil yellow": 232-140-0
- RAL 5015 "sky blue" RGB: 0-124-175
Let's assign these colors to variables in our code below. This way instead of generating the color every time it's needed, you can just use one of the variables that holds its value.
The Measurements
The official measurements for the signpost are specified in the handbook of hiking trail signage.
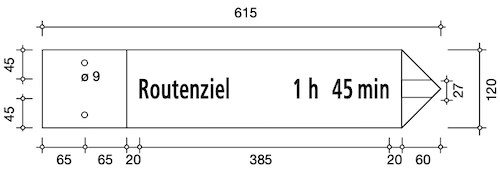
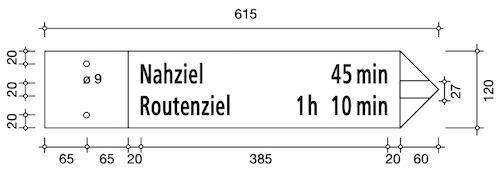
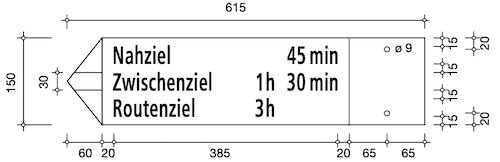
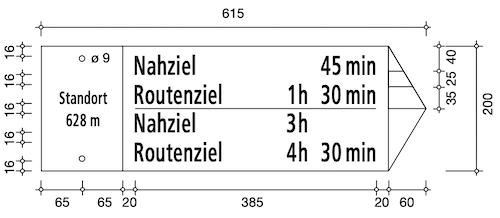
As you can see the measurements for signs with a different number of destinations don't always follow logical rules.
For example, the width of the sign is always the same, but the height sometimes changes.
Let's start by creating constants for the values that remain constant in all signposts.
The variable aspects are:
- the height of the signpost
- the height of the little arrows on the point
- the height of the gaps between destinations (starts as 45, then becomes 20, 15 and rises back to 16)
Let's represent these mappings using dictionaries. In python, a dictionary is a data structure that stores pairs composed by keys and their corresponding values. In a Python dictionary, you use a key to quickly find its associated value.
Fill the incomplete dictionaries below and check out how they are used!
Destinations
On the signpost, destinations are indicated from the top to the bottom, and the maximum number of destinations per signpost is 4. They are divided in 3 categories:
-
Nearest Destination:
Corresponds to the nearest intermediate destination and is listed at the top of the signpost
-
Intermediate Destinations:
Places of greater importance, interfaces with public transport, important junctions and intersections of routes
-
Route Destination:
Corresponds to the end of the route and is listed at the bottom of the signpost.
To each destination is assigned a distance represented in terms of hours and minutes.
How can we represent a destination in terms of its name and distance?
Representing Destinations
We can use a data class. In Python, a data class is a special type of class that is primarily
used to store and manage data. You can create a data class using the @dataclass decorator
from the dataclasses module.
The code below defines a dataclass that can be used to represent destinations:
Helper Functions
Let's implement a collection of small reusable functions to simplify our complex problem.
The render_text Function
The render_text function should generate an
image where the given content is rendered as text
of the given text_color with size points
on a background of color background_color of the
exact same size of the rendered text.
The font of the text should be "ASTRA-frutiger standard", as specified by the original documentation, but due to its rarity it is not available for our text function. Use the font "Roboto Condensed" instead, it is quite similar but still not the same.
Hint: you can also implement a get_background function,
whose purpose is to generate a rectangle with the wanted color,
with the same width and height of the given graphic:
you will find it useful in the future!
You can use graphic_width and graphic_height.
The render_time Function
Each destination has a time information specifying the distance. The time (units h, min) is rounded to 5 min. Starting from a time specification of three hours, specifications with x h 5 min or x h 55 min are rounded to the full hour.
The render_time function should generate an
image where the given minutes are rendered as text of the given text_color
on a background with color background_color of the exact same size of the rendered text.
Ensure that the specifications described are satisfied, by making the correct roundings.
Zeros are not represented, instead the time should be left empty.
Hint: you can convert integers to strings using the python str(integer_value) function!
You can implement the functions suggested below, or come up with your own.
The render_destination Function
Implement the render_destination function so that it returns a graphic representing the
given object of type Destination.
Remember that Destination is a dataclass with attributes name and duration_minutes.
The text should be of the given text_color and have size of the constant content_points px
(we assigned a value to it at the beginning of the activity!).
Routes
A route is a list of destinations, ordered from closest destination to the final route destination.
The render_route Function
Implement the render_route function so that it returns a graphic representing
the given list of destinations.
Notice that the result has no empty space on the top or bottom!
The separator Function
There can be multiple routes developing from a location (maximum four), and they can be represented on a signpost separated by a route separation dash.
The separator function should return a horizontal separation line of the given text_color,
on a background of the given width, height and background_color.
Rendering Multiple Routes
On a signpost there can be just one route or multiple (maximum 4). Each route is a list of destinations, and the maximum number of destinations on a signpost is 4.
The render_routes Function
Implement the render_routes function that renders the given list of routes route_list, where each route is
separated by a separator.
Notice that route_list is a list of routes, therefore a list of lists of destinations (routes).
The result should be enclosed between a top gap and a bottom gap of the given gap_height. There should be gaps on the sides as well,
width gap_height as their width.
IMPORTANT: note that the total width of the result should be width, therefore the width of the text part
should be
width - 2 * gap_heightLocation Field
The location field of a signpost informs about the altitude above sea level and the location name of where the signpost is located.
These are the measurements

The location_info Function
The location_info function should generate a location field with the given location.
You are given a Location dataclass to contain the location's information.
The background color should be traffic_white and the text color should be black.
The points of the text should measure
location_points (defined at the beginning of the activity),
and between the location
name and the location altitude there should be a gap with height 16.
Hiking Trail Signpost
The hiking trail signpost is a yellow sign.
You have developed a right_sign function in the
Swiss Hiking Direction Pointers, that allows you to generate a sign with the wanted
width, height, point_width and color.
Import the right_sign function using your toolbox, and
combine it with the render_routes function and the location_info function,
to generate a hiking trail signpost with the wanted information.
Use the official measurements, assigned to constants and dictionaries at the beginning of the activity, in the Measurements section.
Also implement the count_destinations function that takes a list of routes
and returns the total number of destinations in the routes.
Use it to assert the number of destinations is maximum 4 and minimum 1.
Mountain Trail Signpost
The mountain trail signpost is a yellow sign with a white-red-white point.
You have developed a striped_right_sign function in the
Swiss Hiking Direction Pointers, that allows you to generate a sign
with the wanted
width, height, point_width, arrow_height,
body_color and arrow_color (The body_color is the
color of the rectangular part of the sign).
Import the striped_right_sign function using your toolbox,
and combine it with the render_routes function and the location_info function,
to generate a mountain trail signpost with the wanted information.
Use the official measurements, assigned to constants and dictionaries at the beginning of the activity, in the Measurements section.
Use the count_destinations function you implemented to ensure that
the number of destinations is between 1 and 4.
The red color is constant traffic_red.
Alpine Trail Signpost
The alpine trail signpost is very similar to the mountain trail one, except it is blue with a white-blue-white point.
Use the striped_right_sign function you imported from toolbox,
the render_routes function and the location_info function,
to generate a alpine trail signpost with the wanted information,
pointing to the wanted direction (right if parameter right is True)
Use the official measurements, assigned to constants and dictionaries at the beginning of the activity, in the Measurements section.
Use the count_destinations function you implemented to ensure that
the number of destinations is between 1 and 4.
The blue color is constant sky_blue. Note that the text is written in traffic_white!
What You Learned
You learned about one type of signage you encounter on the Swiss hiking trail network.xw
You also (hopefully) practiced to structure your code so you can reuse functionality. Implementing all those helper functions in the beginning may have seemed useless or confusing, but in the end it allowed you to decompose a bigger problem into simpler and reusable code.
This activity has been created by LuCE Research Lab and is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0.
Swiss Hiking Signposts

PyTamaro is a project created by the Lugano Computing Education Research Lab at the Software Institute of USI
Privacy Policy • Platform Version 50af0ba5 (Mon, 23 Feb 2026 11:44:41 GMT)
